USD/JPY lurches higher after Powell splashes cold water on rate cut hopes

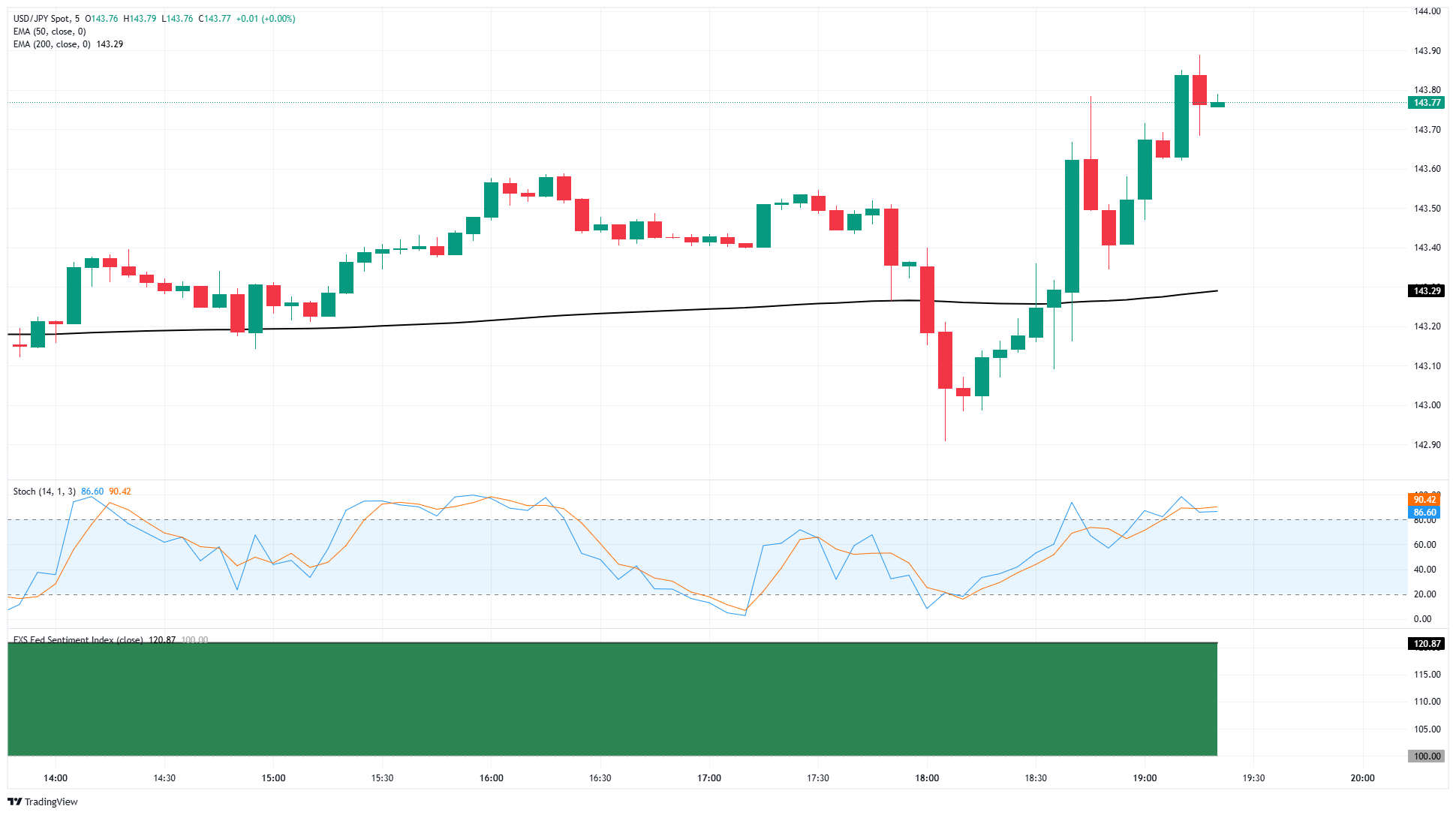
- The USD/JPY fell into the 143.00 region after Fed rates were strengthened on Wednesday.
- The market reliance of a cut rate in July accelerated after the Fed warned of increasing economic risks.
- The market sentiment is a reversible course after the Fed Chair Powell warned that tariffs make it difficult for the Fed to achieve its goals.
USD/JPY took a header on Wednesday, which fell to 143.00 in Intraday trading after Federal Reserve (Fed) held Rates Stable at 4.25-4.5%, as many investors expect. The market forecasts of an upcoming Fed pivot on a rate cutting increase after the warning of policy manufacturers of increasing economic risks. However, Fed chair Jerome Powell looked back at the market was flowing hard after note that the risks for the Fed to maintain the wait-and-see stance remain very low.
Based on the recent announcement of the Fed rate, policy manufacturers have indicated that even if US activity and economic activity are generally stable, the dangers of labor and labor have increased. Increasing this risk comes primarily from the uncertainty related to the tariffs and policies of the US trading. The concerns that Fed officials have expressed about economic risks have been to -fueled market expectations for potential rates in rate, resulting in an unexpected advanced appetite.
Read more Fed News here: We don't have to rush
The sentiment refused the market after the Fed Chair Jerome Powell's press conference. He said that if the tariffs on the US trade, they would block Fed's goals about inflation and work for the rest of the year. Powell also warned that the ongoing uncertainty of the policy would likely lead to the Fed to maintain the 'wait-and-see' stance at interest rates. Despite significant damage to consumer and business confidence caused by Trump administration's tariff policies, poor economic data has shown a slight negative impact, which complicates the Fed's ability to justify any immediate change in interest rates.
According to the CME's Fedwatch tool, market rates continue to expect a quarter-point rate cut in July; However, the likelihood of another rate that handles in July increased to 30%, which sinks wide expectations for a smooth transition to another phase of cutting rates.
USD/JPY 5 Minute Chart
Fed faqs
The US financial policy is shaped by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and promote full work. Its main tool to achieve these goals is by organizing interest rates. When prices rise rapidly and inflation is above the Fed's 2% target, it increases interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US dollar (USD) because it makes the US more attractive for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, with a greenback weight.
The Federal Reserve (FED) holds eight policy meetings a year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes financial policy decisions. The FOMC was attended by twelve Fed officials-the seven members of the Board of Managers, the President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional reserve bank presidents, which served a one-year term on a spinning basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can make a policy named EASING (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed greatly increases the flow of credit to a stuck financial system. This is a policy proposal that is not standard used during crises or when inflation is very low. This was the weapon of fed selection during the great financial crisis in 2008. It involves printing the Fed more dollars and using them to buy high -grade high -grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US dollar.
The quantity of tightening (QT) is the Reverse process of QE, where the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not re -consist of the bonds from its bonds, to buy new bonds. This is usually positive for the US dollar value.




