A Study on Task Design and User Interaction in VR Navigation
Those with -set:
(1) Rafael Kuffner Dos Anjos;
(2) Joao Madeiras Pereira.
Link
Abstract and 1 Introduction
2 relevant work and 2.1 virtual avatar
2.2 Point Cloud Visualization
3 test design and 3.1 setup
3.2 User Representations
3.3 Procedure
3.4 virtual environment and 3.5 descriptions of tasks
3.6 Questions and 3.7 Participants
4 results and discussions, and 4.1 user preferences
4.2 Performance of the work
4.3 Discussion
5 Conclusions and References
3.3 Procedure
The test is divided into eight stages: 1) introduction to the study and application of the pre-test questionnaire; 2) Explanation about tasks and each of users' representations 3) device adjustment for comfort; 4) Calibration methods; 6) work implementation; 7) Post-test questionnaire application; 8) and a semi-structured interview.
At first, we explained the test goals. Then, users completed a pre-use questionnaire to raise the profile of participants regarding previous experience with related technologies (HMDS, Virtual Avatar, etc.).
Subsequently, we showed a brief description of the tasks and representations used. Moreover, we show users in the work of calibration. This procedure was performed to calibrate the monitoring system between the HMDS and the deep sensor. Then, for the user to become familiar with the methods, users conducted a task in a training scenario, where they could freely explore the virtual environment and were familiar with setup and each of the representations.
After performing the training task, users reached a fixed object in the environment and users conducted the test task. Then a questionnaire is given to users for some issues with the user experience. These steps are taken for each other in combination with test conditions (perspective and representation) of a total of 12 permutations. Avatar's represented representation was changed to each test, following a Latin Square repair, to prevent bias results.
3.4 virtual environment
The selected environment is based on stealth view, which is obtained at the Unity Asset store[1]. This scene has been modified to remove visual clutter, for not interfering with the objectives of the test, stealing the user's attention.
We also include the environment a representation of Kinect tracking limits with a red square, where the user is free to walk.
3.5 Description of activities
Due to the reduced size of the monitored space (4 meters 4 meters), we decided to divide the test into four activities. For each of the tasks, the user must reach a specific point at the end of the monitored space, where he or she needs to reach a colored sphere (either red or green) with their hand to pass on to the next task. Tasks are selected based on natural activities such as walking, avoiding barriers and capturing moving objects based on previous work [28].
After that, he turned his body to deal with the next work, until the trial was over. In the following subscribing we display and explain each of the tasks in more detail.
3.5.1 First Activity
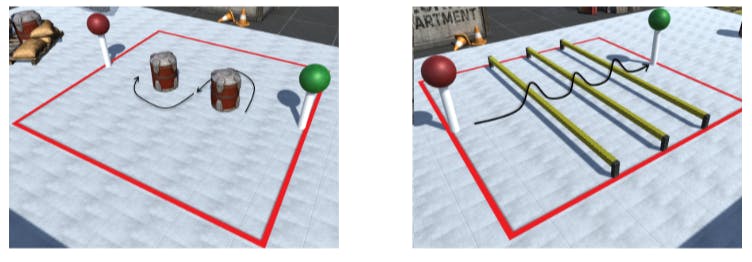
In this work, after reaching the green object the user turns his body and needs to go around the barrel, first by the right, then to the left until they reach the read target object. Figure 3a describes the first task.
3.5.2 Second task
In the second task, the user needs to avoid each of the yellow bars by raising their feet (or jumping) until they reach the green target object (Fig. 3b).
3.5.3 Third Tasks
The user needs to avoid the yellow bar by going under it. This bar is adjusted according to the height of the user, which is estimated using the distance between the head and toes when the user starts the test. The bar is placed 12 centimeters below the total user height (Fig. 3C).
3.5.4 Fourth Tasks
In the final task the user must reach a small red square located in front of the red target object. This work is a reflex -based task made up of four balls thrown toward the user of a cannon (Fig. 3D). To succeed in this work they need to stop them with their body. All the balls were thrown at the same speed, only the point was thrown at them. The first ball was thrown toward the user's chest, second and third towards the user's right and left arm. The fourth ball is thrown to the right side of the user but he has to walk right to reach it.
3.6 questions
To assemble users' profiles, preferences are conducted a pre-test questionnaire. For assessing human factors such as convenience, feeling of emblem and satisfaction, a post-test questionnaire was performed. The post-test questionnaire consists of a list of 11 statements followed by a Likert Scale of 6 values, where 1 means the user disagrees fully in the statement and 6 means he or she is fully agreed, such as summary in Table 1. The first four questions, based on previous task [7]. The following questions are made to assess each other of the subtasks and fatigue.
In addition to the questionnaire, we conducted a semi-structured interview to obtain participants' perception of the accomplishments, clarify about their answers to the post-test questionnaire and get improvement suggestions.
3.7 Participants
For this test we chose 24 participants, 5 of which were female. The age of users varies from 21 to 35 years. As for the experience, most users have had a previous experience in 3D applications such as games and modeling systems. Most of them have experience with a previous experience on head-mounted displays.
[1]